Authors: Jie Liu, Yitong Dong, Zhengxin Ma, Zhilu Rao, Xuejing Zheng, Keyong Tang
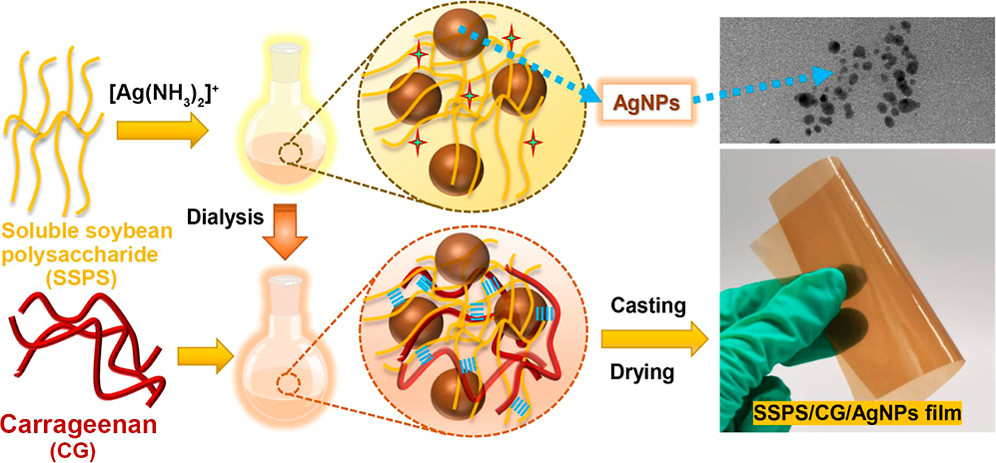
This study aimed to develop nanocomposite films based on a soluble soybean polysaccharide (SSPS), carrageenan (CG), and green synthesized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) by a solution casting technique. AgNPs were obtained by reducing a silver–ammonia complex using a SSPS as both a stabilizing and reducing agent, which was confirmed by UV–vis spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. CG was introduced into the SSPS/AgNP matrix as a reinforcing component to strengthen the nanocomposite films. The results indicate that the addition of CG led to significantly enhanced mechanical properties, thermal stability, and water resistance of the films. The XRD and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy results reveal strong interactions between AgNPs and polysaccharide chains. Compared with the SSPS/CG films without AgNPs, the SSPS/CG/AgNP nanocomposite films exhibited antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. The results suggest that the SSPS/CG/AgNP antibacterial nanocomposite films have great potential in food and pharmaceutical packaging applications.
全文链接:https://doi.org/10.1021/acsapm.2c00635